| Type |
Description |
Diagram |
|
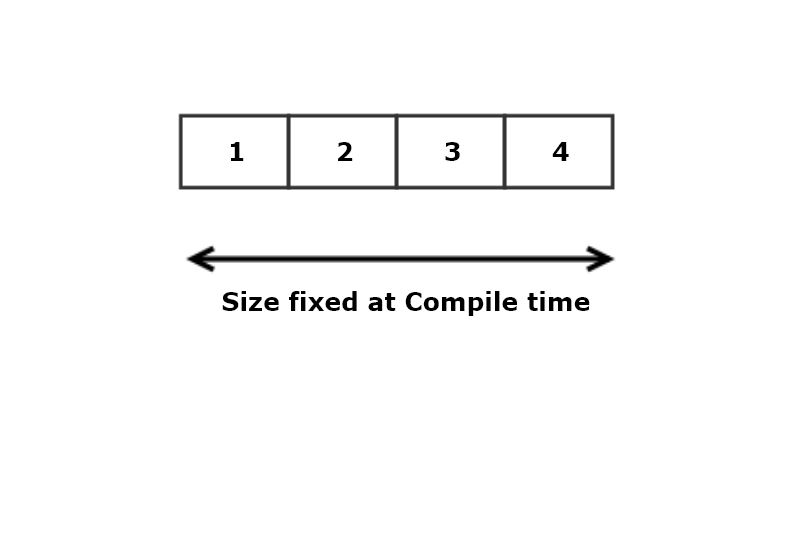
array<T, N>
|
Collection of instances of type T residing in contiguous stack memory.
-
create array:
let mut array: [i32; 3] = [1, 2, 3];
array[1] = -2;
-
An array is a copy type, provided that T is copy.
-
Code demo:
create and display arrays
|
|
|
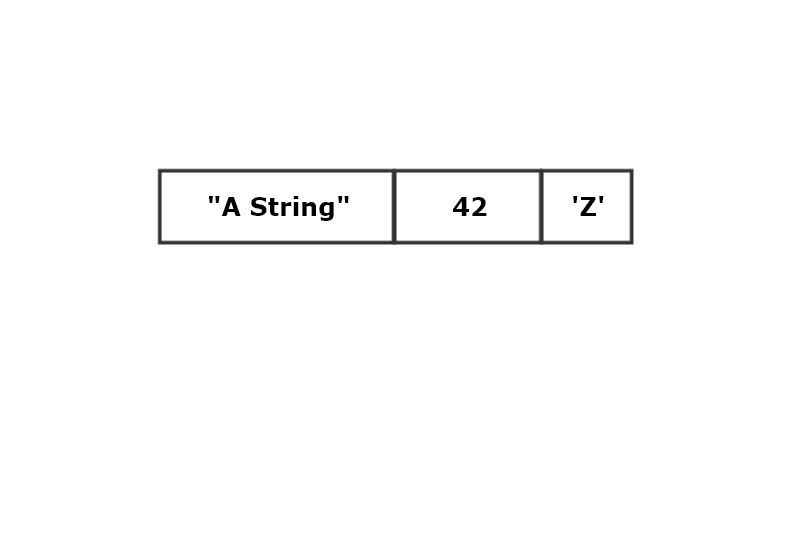
tuple<T, U, V, ...>
|
Collection of instances of possibly different types residing in contiguous memory.
-
create tupl:
let t: (&'static str, i32, char) =
("a tuple", 42, 'Z');
let mut u = t;
u.1 = -42;
-
Tupls are copy if, and only if, each member is copy.
-
Code demo:
create and display tuples
|
|
|
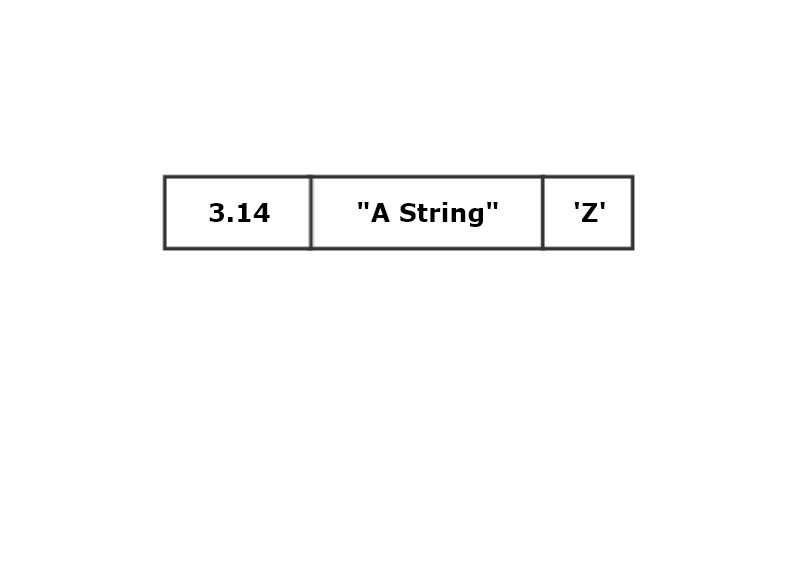
Struct<T, U, V, ...>
|
Collection of instances of possibly different types residing in contiguous memory.
-
create struct:
struct MyType { d: f64, ... }
let s = MyType { d: 3.14, ... };
let t = s;
-
Structs are copy types if, and only if, each member is copy.
-
Code demo:
create and display structs
|
|
|
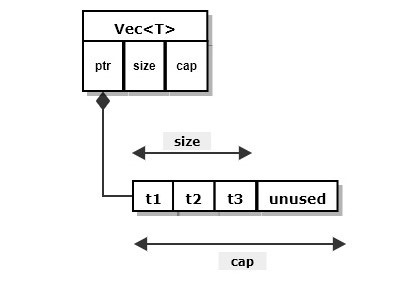
Vec<T>
|
Collection of instances of type T residing in contiguous heap memory.
-
consists of control block in stack holding pointer to array of T instances in heap
-
reallocates heap memory to accept new instance when capacity is full
-
create vector:
let v = Vec::<int>::new();
let w: Vec<T> = vec![t1, t2, t3];
-
v and w are dropped, returning resources, when they go out of scope.
-
Code demo:
create and display vectors
|
|
|
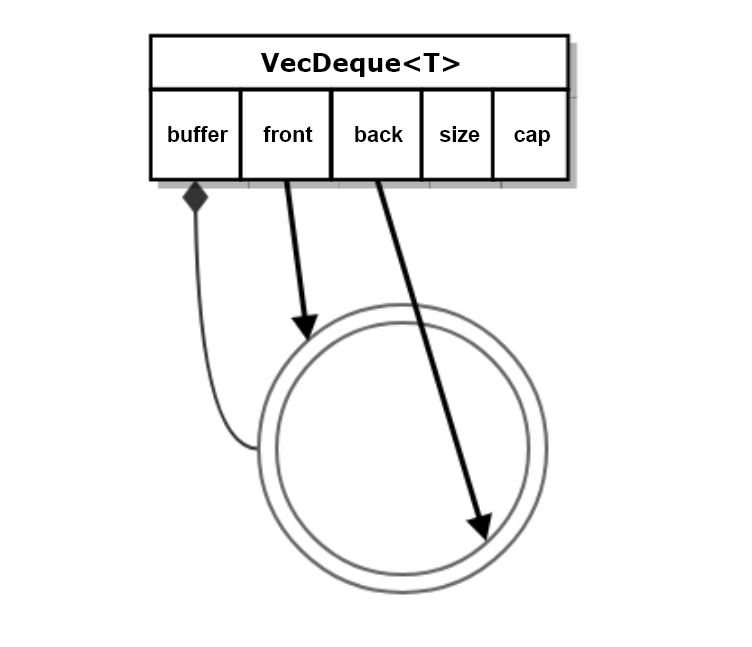
VecDeque<T>
|
Collection of instances of type T residing in a circular buffer in heap memory.
-
consists of control block in stack holding pointer to circular buffer of T instances in heap
-
Control block contains references to the front and back of the VecDeque.
-
reallocates heap memory to accept new instance when capacity is full
-
create queue:
let v = VecDec::<T>::new();
v.push_back(t1); v.push_back(t2); let u = v.pop_front();
-
v and u are dropped, returning resources, when they go out of scope.
-
Code demo:
create and display vecdeque
|
|
|
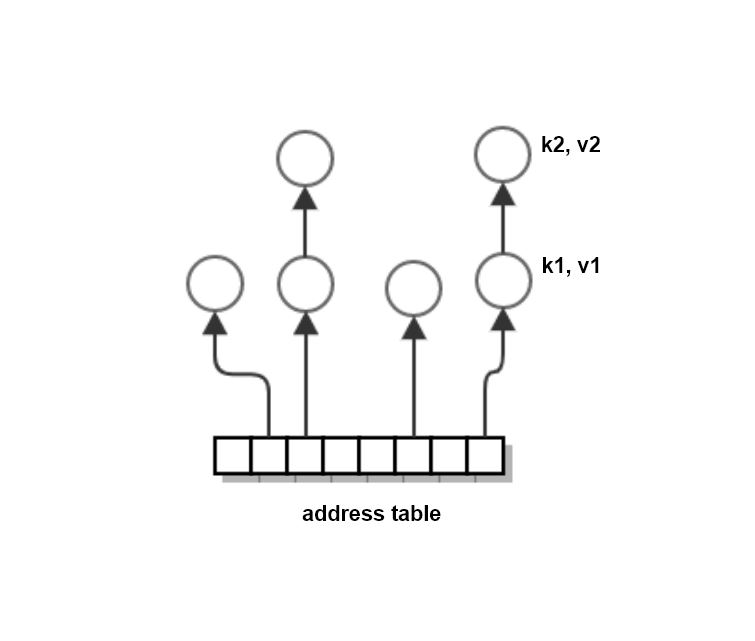
HashMap<K,V>
|
Collection of buckets (linked list of key-value pairs) rooted in table in heap memory.
-
Consists of control block in stack holding pointer to address table of buckets in heap
-
Hash function used to calculate table address from key.
-
If hash yields address with existing bucket, key-value pair added to bucket list.
-
Reallocates table memory when table bucket count approaches table size.
-
create hashmap:
let h = HashMap::<K,V>::new();
h.insert(k,v);
-
table and all bucket elements are dropped when they go out of scope.
-
Code demo:
create and display HashMap
|
|
|
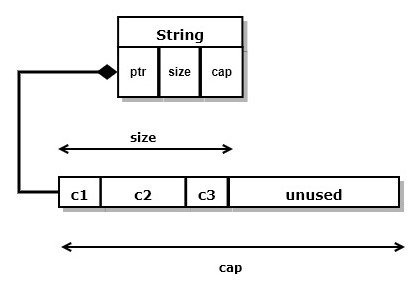
String
|
Collection of utf-8 characters residing in contiguous heap memory.
-
consists of control block in stack holding ptr to contiguous heap memory allocation.
-
a utf-8 character may occupy from 1 to 4 bytes, allowing a large collection of
language sets, e.g., ASCII, Unicode, Kanji, Arabic, ...
-
The item above means that Rust std::String instances cannot be indexed. There is a
string iterator, called chars(), that understands byte sequences that define
utf-8 character boundaries.
let s = String::from("a literal string");
let c2 = s.chars().nth(4).unwrap();
-
reallocates heap memory to accept new character(s) when capacity is full
-
create String:
let s = String::new();
let t = String::from("a string");
-
s and t are dropped, returning resources, when they go out of scope.
-
Code demo:
create and manipulate String and str
|
|
|
str
|
str is a copy type that represents a literal string in contiguous block of memory
-
converting between str and String:
let s = "an ordered collection of utf-8 characters";
let t = String::from(s);
let u = &S;
-
Literal strings are almost always used via a reference, e.g., &s
-
Sample code in Rust Playground:
copy str demo
|

|







